https://openreview.net/forum?id=IW1PR7vEBf#discussion
LLM2Vec: Large Language Models Are Secretly Powerful Text Encoders
Large decoder-only language models (LLMs) are the state-of-the-art models on most of today's NLP tasks and benchmarks. Yet, the community is only slowly adopting these models for text embedding...
openreview.net
LLM2Vec의 논문은 잘 만들어진 llm decoder를 통해 효과적인 embedding으로 사용하는 간단한 unsupervised 방법을 제시합니다.
Introduction
Text embedding model은 natural language로 구성되어있는 semantic content를 vector representation으로 변환할 수 있어서 semantic textual similarity, information retrieval, clustering과 같은 다양한 NLP task에 활용될 수 있습니다.
이전까진 이런 text embedding model은 사전 학습된 bidirectional encoder (e.g., BERT)나 encoder-decoder(e.g.,T5)로 사용되었고 이 때 weakly-, fully-supervised contrastive learning으로 이루어져 있는 여러 단계의 pipeline을 통해 학습되었습니다. 최근에 들어서야 많은 연구가 되고 있는 decoder-only LLM이 embedding text에 사용되고 있습니다.
저자는 이렇게 decoder-only LLM이 text embedding task에 많이 활용되지 못했던 이유를 decoder model에 존재하는 'causal attention mechanism' 때문이라고 주장합니다. 이 causal attention이 풍부한 contextualized representation을 만들어내지못하게 한다고 합니다. 당연하게, 어떤 layer에서도 position i에 있는 token은 그 앞에 있는 0,1,...,i-1의 position에 있는 token들에 대한 representation에만 영향을 받게 되고 결국 이는 token interaction을 제한시키기 때문입니다. 물론 이런 특징은 decoder의 주요 능력인 generative capability에선 꼭 필요한 과정이지만, text embedding을 표현하는 데에 있어선 sub-optimal의 성능을 낼 수 밖에 없습니다.
그러나 이러한 문제만 해결된다면 decoder-only model을 text embedding task에 사용하는 것은 encoder-only model을 text embedding task에 사용하는 것보다 훨씬 더 많은 장점이 존재하게 됩니다.
1. pre-training 하는 동안 encoder-only model은 전체 token 중 일부를 masking해서 masking된 token만 학습하게 되는 반면, decoder-only model은 하나씩 token을 생성하기 때문에 같은 sample의 size를 통해서 훨씬 더 많은 것을 학습시킬 수 있습니다. 즉 훨씬 sample-efficient합니다.
2. decoder-only model이 encoder-only model보다 훨씬 더 많은 연구가 진행되고 있습니다.
3. 최근에는 instruction fine-tuning이나 human preference 학습들로 인해, decoder-only LLM들은 instruction following (LLM이 제시하는 instruction 말 잘듣는 것)이 가능해졌고, 이로 인해 다양한 task에 generalize되는 universal embedding 모델로 적합합니다.
그렇다면 왜 encoder보다 decoder가 더 많이 발전되고 있을까?
- model이 scaling up 되는 만큼 decoder에 비해 성능이 좋아지지 않음.
- sample efficient하지 않음
- decoder는 generation에 강해서 확장성이 좋음. 즉 encoder는 embedding말고 쓰는 곳이 많지 않음
이 논문에선, LLM2Vec이라는 어떤 pre-trained decoder-only LLM이든 text encoder로 변환할 수 있는 간단한 unsupervised 방법을 제시합니다.
LLM2Vec

LLM2Vec는 크게 3가지 방법으로 구성되어 있습니다.
1. Enabling bidirectional attention
가장 먼저 해야 할 일은 기존에는 decoder-only LLM에서 현재 시점보다 이전 token들만 참조하는 causal attention을 bidirectional attention으로 변환하는 일입니다. 이를 위해 모두 1로 이루어진 attention mask(all-ones matrix)로 바꿔줍니다. 이렇게 바꿔준다면 모든 token이 sequence 내에 모든 token에 접근할 수 있게 되어 bidirectional LLM으로 변하게 됩니다. (BERT처럼 pseudo-bidirectional 모델로 바꾼 것). bidirectional attention으로 변환하긴 했지만 당연히 기존의 decoder-only llm은 bidirectional하게 attention하지 않도록 훈련되었기 때문에 성능이 좋지 않을 수 있고 실제로 실험해보니 이렇게 단순히 attention mask를 바꾸는 것만으론 오히려 embedding 성능이 나빠지게 된다고 합니다. 이유는 당연히 모델이 훈련 당시에 이후의 token들을 참조하지 않는 방식에 최적화되어 있기 때문입니다. 결국 새로운 attention 구조에 맞는 학습 방식으로 모델을 적응시켜야 합니다.
2. Masked next token prediction
LLM2Vec에서 bidirectional attention을 실제로 효과있게 하기 위해 간단한 기법인 masked next token prediction (MNTP) 학습 기법을 사용하게 됩니다. MNTP는 masked language modeling (MLM)과 next token prediction(NPT) 이 두 가지 학습 방식을 결합한 새로운 학습 기법입니다.
input sentence x=(x1,x2,...,xn)이 있다고 해봅시다. 전체 입력 중 일부 token을 random하게 masking을 진행합니다. x4를 [MASK] 했다고 하면, 이제 모델을 해당 [MASK] 위치의 정답 token을 맞추는 방식입니다. 그런데 이 때 정답을 예측하는 위치가 [MASK] 그 자체가 아니라, 그 이전 토큰(i-1)의 representation에서 예측합니다. 즉, x4가 masking 되어 있으면, input sequence의 모든 token을 보고 예측하는 게 아닌 x3의 output vector로 x4를 예측해야 합니다. 이는 기존의 decoder-style의 next-token prediction과 유사한 형식을 가지면서도 masking을 통해 bidirectional context를 활용할 수 있도록 합니다.
이전 token으로 masking된 위치를 예측하는건데 어떻게 bidirectional attention을 사용할 수 있다는 걸까?
: 모델이 이전 token의 representation을 통해 prediction을 한다고 하더라도 이전 token의 output이 이미 문장의 전체 정보를 본 상태에서 만들어지기 때문입니다.
3. Unsupervised contrastive learning
물론 위의 2가지 방식으로 어떤 decoder-only LLM이든 모두 word-level task에 적합한 encoder로 변형할 수 있긴 하지만, sequence를 표현하기엔 아직 한계가 있습니다. pre-training 단계에서 next sentence prediction을 하게 되는 bidirectional encoder와 달리 decoder-only LLM은 직접적으로 전체 sequence의 문맥을 파악하는 학습을 진행하지 않습니다. sequence까지 잘 파악하기 위해 SimCSE를 통해 unsupervised contrastive learning을 진행합니다. input sentence가 주어지면, 각각 독립적으로 dropout mask가 sampling된 model을 두 번 거치게 되고, 이렇게 되면 하나의 sentence에 대해서 2개의 다른 representation을 얻을 수 있게 됩니다. 여기서 모델은 하나의 문장에 대해 다른 representation간의 similarity는 maximize하고 batch 내의 각각 다른 문장의 representation에 대해선 similarity를 minimize하도록 합니다. 그렇기 때문에 여기선 별도의 sentence pair data가 추가될 필요 없습니다. 그리고 최종적으로 sentence representation을 얻기 위해 word representation에 대해 pooling operation을 사용합니다.
즉, 1(bidirectional attention), 2(MNTP)는 word-level task의 성능을 높이기 위한 것이고
3(unsupervised contrastive learning)은 sentence-level task의 성능을 높이기 위한 것이라고 보면 됩니다.
조금 더 디테일하게 살펴보자면
- Model
총 4개의 다른 decoder-only LLM (1.3B부터 7B parameter까지)에 대해 실험을 진행했습니다.
Sheared-LLaMA-1.3B, Llama-2-7B-chat, Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2, Meta-LLaMA-3-8B.
이 LLM model들에 대해 각각 word-level task와 sentence-level task evaluation 진행
- Training data
English Wikipedia에서 갖고온 data 사용해서 MNTP와 unsupervised SimCSE에 대해 진행했습니다.
이 Wikipedia 데이터는 기존의 LLM들이 pre-training할 때 학습된 데이터로, MNTP와 unsupervised SimCSE 학습을 진행하는 과정에서 새로운 데이터로 인해 새로운 지식을 얻는 것을 방지하고자 선택했다고 합니다.
구체적으론 MNTP step에선 Wikitext-103 dataset을, unsupervised SimCSE step에선 Wikipedia sentence의 subset을 사용했습니다.
- Masked next token prediction
MNTP는 기존에 존재하는 방법을 따랐다고 합니다. 그리고 여기서 실험하는 model은 masking에 대한 special token이 따로 없기 때문에 mask token으로 underscore(_)를 사용했다고 합니다. 이전 token의 representation을 활용해서 masking된 token을 예측하도록 했고 이 때 LoRA를 사용해 fine-tune 했습니다. masked token을 예측하되, 그 바로 이전 token의 representation을 사용해서 예측하도록 설계했습니다. 즉, masked token을 예측하는 방식은 encoder-style이고, decoder-only 모델의 causal 구조에 맞춰, masked token의 이전 위치의 hidden representation을 이용해 예측합니다 .그래서 decoder 구조의 학습방식과 alignment가 잘 맞는다고 할 수 있습니다. 모든 모델에 대해 batch size 32, 1000 step, single 80GB A100 GPU 사용합니다. 7B, 8B model에 대해 training은 100분내에 학습시킬 수 있습니다.
- Unsupervised contrastive learning
여기선 SimCSE 방법을 사용했습니다. 같은 input sequence에 대해 LLM을 dropout을 다르게 해서 뽑아낸 representation을 positive example로 사용해고, batch 내의 다른 sequence들을 negative로 사용합니다. MNTP와 unsupervised contrastive learning을 모두 적용하기 위해, base 모델에 먼저 MNTP LoRA weight를 merge하고 새로운 LoRA parameter로 SimCSE를 fine-tuning합니다. 그렇게 되면 contrastive learning을 할 때 이전 step의 knowledge를 보유한채로 학습시킬 수 있기 때문입니다. MNTP와 비슷하게 1000 step으로 학습시켰고, 7B,8B model에 대해 batch size 128로 single 80GB A100 GPU에 대해 training에 대해 3시간이 걸렸습니다.
LLM2Vec-transformed models are strong unsupervised text embedders
evaluation은 크게 word-level task와 sequence-level task에 대해 이루어졌습니다.
[word-level tasks]

Task 3개 : chunking, named-entity recognition(NER), part-of-speech tagging(POS)
- Chunking (Shallow Parsing)
: 문장을 phrase(어구) 단위로 분할 (명사구, 동사구 등)
- NER (named-entity recognition)
: 사람, 장소, 조직, 날짜 같은 고유명사(개체명)을 인식하고 범주화
- POS (Part-of-Speech)
: 각 단어가 문장에서 어떤 품사인지 분류
Benchmark : CoNLL-2003
각 input sentence를 embedding하고 전체 representation을 고정시키고 task마다 task-specific linear classifier를 추가해 학습을 진행. 이렇게 학습한 LLM2Vec-transformed model을 현재 encoder-only model의 SOTA인 DeBAERTa-v3-large와 비교.
Results
- 3개의 모든 task에 대해서 causal attention으로 token representation 만드는 것이 이미 기존의 encoder-only baseline보다 앞섰습니다. 당연한 결과인게 이 논문에서 학습시킨 모델 자체가 훨씬 크고 훨씬 더 많은 데이터로 학습되었기 때문입니다.
- 대부분의 케이스에선 예상한대로 단순히 bidirectional attention을 적용하는 건 대부분 성능을 저하시켰습니다.
- LLM2Vec-transformed model을 봤을 때 모든 모델과 task에 대해 MNTP를 적용시키면 성능이 올라갑니다.
- (SimCSE+MNTP)와 (MNTP)를 비교했을 때만 MNTP만 적용시켰을 때 성능이 더 좋았습니다. 이 말은 SimCSE는 word-level task를 위한 과정이 아닌 sequence-level task에 대한 representation을 적용했다고 볼 수 있습니다.
[sequence-level tasks]
MTEB(massive text embedding benchmark)에 대해 진행했고, MTEB는 56개의 dataset을 포함해 다양한 embedding task category로 이루어져 있습니다. 각 method에 대해 가장 좋은 pooling method를 선택하기 위해, MTEB의 각 카테고리에 대해 대표적인 task로 이루어져있는 15개의 task subset으로 진행했습니다.
Setup
이전 연구들과 같이 task-specific instruction으로 evaluation 진행했습니다. instruction은 query에만 추가됐고, symmetric task에 대해서, query와 document에 같은 instruction이 사용됩니다. (weighted) mean pooling을 할 땐 instruction token을 제외했습니다.
baseline으로 unsupervised BERT model, Echo embedding과 비교했습니다. Echo embedding과 같은 모델과 instruction을 사용합니다. Echo approach는 causal information flow의 limitation을 해결하기 위해 input를 2개로 이어붙여서 두번째의 input에서 pooling하는 기법입니다.
Results on our 15 task subset of MTEB

위 figure는 다양한 pooling 방법에 대한 실험결과입니다. text embedding 사용할 때 단순히 causal attention을 사용하는 것(original version)은 sub-optimal임을 볼 수 있습니다. 그리고 EOS pooling이랑 (weighted) mean pooling 비교했을 때 mean pooling이 더 좋습니다. 추가 학습없이 단순히 bidirectional attention 적용하는 건 word-level task 때와 마찬가지로 성능을 저하시킬 수 있습니다.
LLM2Vec-transformed model에 대해, MNTP 적용하면 성능이 오르고, SimCSE까지 적용하면 성능이 더 많이 오릅니다.
Results on full MTEB

decoder-only LLM모델에 LLM2Vec 적용시킨 결과.
How does LLM2Vec affect a model?
LLM2Vec helps models to capture information from future tokens
LLM2Vec-transformed model들이 초키 token의 embedding이 future token의 영향을 얼마나 활용하는지에 대해 알아보기 위해, 같은 prefix를 공유하는 sentence간의 similarity를 분석해 model이 얼마나 잘 수행하는지 알아봅니다.
Setup
- synthetic dataset으로 평가진행. 35 sentence triple이 존재.

이 때 B_i와 C_i는 비슷한 의미를 갖고 B_i와 D_i는 그렇지 않음.
즉 decoder 모델이 초기 token (A_i) embedding에서 미래 context (B_i, C_i,D_i) 정보를 얼마나 반영하는지 간접적으로 측정하기 위한 평가.
- q_i=(A_i, B_i) : 원래 문장 (query)
- s+_i=(A_i,C_i) : 의미가 비슷한 문장 (positive)
- s-_i=(A_i,D_i) : 의미가 다른 문장 (negative)
여기서 A_i가 문장의 공통 prefix가 됨.
각 문장의 embedding은 A_i 부분만 pooling해서 확인해봅니다. future token (B_i, C_i, D_i)의 embedding은 직접 포함되지 않습니다.
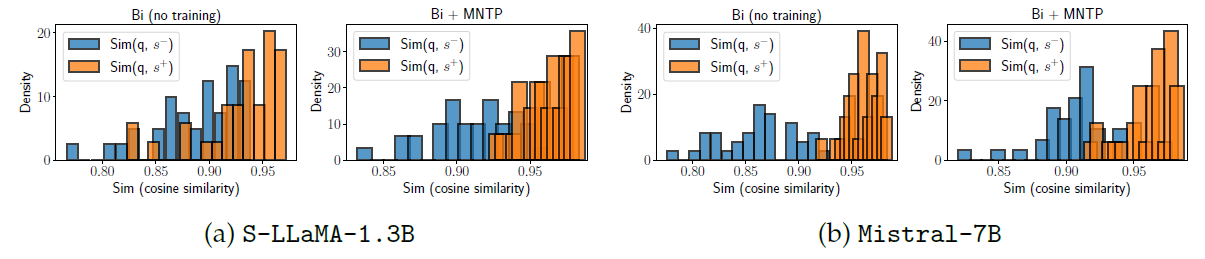
결과를 보면 S-LLaMA-1.3B는 MNTP를 적용하게 되면 positive와는 similairty가 높아지고 negative와는 similarity가 낮아지는 차이가 더 극명하게 되었습니다. Mistral은 MNTP 적용과 상관없이 negative보다 positive sample가 similarity가 더 높습니다.
Why does bidirectional attention without training work for Mistral models?
그렇다면 왜 Mistral model에 대해선 이러한 현상이 나타날까요?
여기선 bidirectional attention이 model의 representation에 어떤 영향을 주는지 분석해봅니다.
Setup
각 모델에 하나의 input sequence를 넣고 모든 layer에서 모든 token에 대한 hidden representation을 계산합니다. 이 때 causal attention (H^c_l)을 사용했을 경우와 bidirectioanl attention (H^bi_l)을 사용했을 경우에 대해 모두 hidden representation을 뽑아냅니다. 모든 layer에 대해 causal과 bidirectional attention을 사용한 representation간의 cosine similairty를 계산합니다. sim(H^c_l, H^bi_l). 대부분의 layer에서, similarity가 낮게 나온다면 이는 training없이 단순히 bidirectional attention을 적용하는건 상당히 다른 representation을 나타낸다고 볼 수 있습니다.
Results

결과를 보면 (a),(b)는 실제로 training없이 bidirectional attention을 적용했을 때 대부분의 모든 layer와 token position에 대해 낮은 similarity를 보였습니다. 반면 (c)Mistral의 경우엔 높은 cosine similarity를 보였습니다. 즉 mistral에선 causal attention을 bidirectional attention으로 바꿔도 별 차이가 없다는 것을 알 수 있습니다. 이런 현상에 대해, 논문에선 Mistral이 bidirectional attention과 같은 형태(prefix language modeling과 같은)로 pre-trained 됐을 거라고 주장합니다.
Combining LLM2Vec with supervised contrastive learning
마지막 분석은 LLM2Vec에 supervised contrastive learing을 진행해보는 것입니다. (기존엔 SimCSE라는 unsupervised contrastive learning으로 fine-tuning함)
LLM2Vec leads to strong performance on the MTEB leaderboard
Setup
supervised training에서, E5 dataset과 비슷하게 학습시킵니다. 같은 instruction을 가진 쌍은 positive로, 다른 instruction을 가진 쌍은 hard negative가 됩니다. 여기서도 LoRA 기반 fine-tuning으로 supervised contrastive learning을 학습했고 LoRA 가중치만 업데이트하게 됩니다. supervised setting에서도 LoRA로 fine-tuning 진행합니다.
Results

모든 model에 대해 LLM2Vec 변형버전이 Uni+weighted mean baseline보다 성능이 올랐습니다. 예상처럼, supervised training에선 unsupervised SimCSE는 크게 중요하지 않습니다. 그럼에도 불구하고 SimCSE를 사용하는 이유는 훨씬 sample-efficient하기 때문입니다.
LLM2Vec leads to more sample-efficient training
Setup
LLM2Vec-transformed model의 sample-efficiency 보이기 위해 25 training step마다 checkpoint를 찍고 평가했습니다.
Results
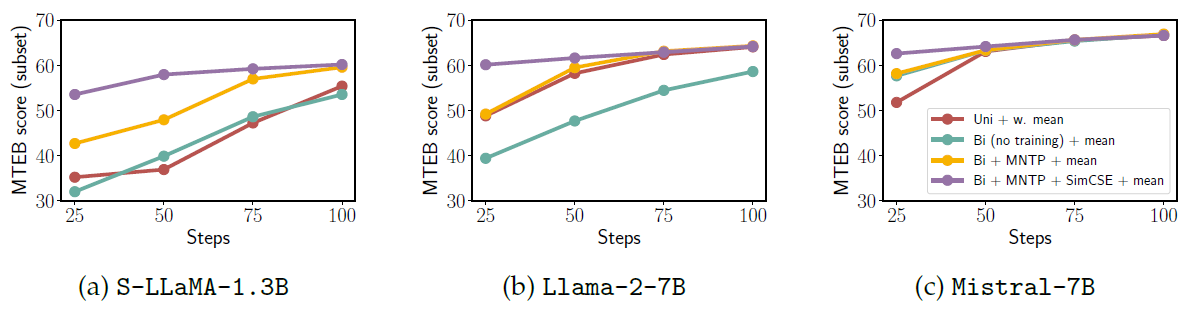
LLM2Vec 모델이 훨씬 더 빨리 좋은 성능을 보였습니다. 이는 MNTP+SimCSE를 하는 것이 sample-efficiency를 높인다고 볼 수 있습니다.



